Depression and Technology
Laboratory tests can confirm heart disease or cancer but previously, they could not diagnose psychiatric conditions. That is all in the past now as scientists claim that technology can now physically distinguish between the different kinds of mental illnesses as well as depression in order to enable tailored therapies for individuals.This breaks the longstanding tendency of diagnosing psychiatric disorders by symptoms only. However this discovery is subject to confirmation.
Brain imaging such as positron emission tomography (PET) scan compares brain activity during depression with normal brain activity. The more the blue and green colors, the more likelihood of depression due to decreased brain activity signaled by decreased white and yellow areas.
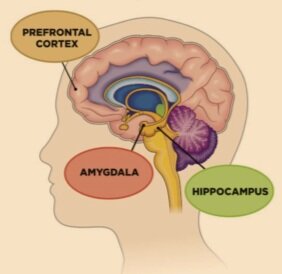
Studies have also shown that the hippocampus an area of the brain responsible for memory and emotion shrinks in people with recurrent and poorly treated depression. It is larger in normal people and those taking antidepressants.
This is the same for the grey matter in the brain of depressed people, which is less than 20% as compared to that of normal people. After 8 weeks of treatment, the patients grey matter increased and eventually went to normal after recovery.
The amygdala is one of the parts of the brain associated with emotions such as anger pleasure, sorrow, fear or sexual feelings. When a person recalls emotional feelings, the amygdala is triggered especially in frightening situations. Its activities become rampant according to oxford centre scientists who in a study showed negative images to both the depressed and non depressed as they scanned their brains (amygdale). Depressed people tended to exaggerate the images they saw, making a mountain out of a mole hill. They tended to pick negative cues according to their amygdala.
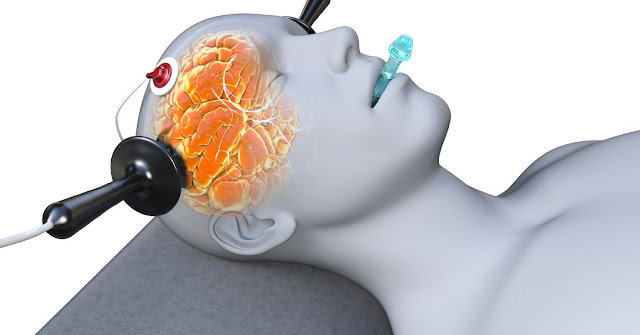
The advancement is not only in the technological diagnosis but also in treatment. Electro convulsive therapy can be used to treat severe depression. The patient is given anesthesia to relax the muscles and electrodes are placed on their scalp in order for controlled electric current to trigger a seizure in the brain to relieve symptoms of depression. However experts warn it can cause short term memory loss.
Vagus nerve stimulator (VNS) is a surgical implant the size of a 20 shilling coin in the upper chest below the collar bone, which is attached to a stimulating wire up the neck and to the brain where it connects to mood regulating areas, sleep, appetite or motivation. The device sends electric pulses to the nerve which are transmitted to the brain at regular intervals. Though its effects may be felt several months later, 30% of patients show improvement in mood, sleep, energy, motivation and overall quality of life. Risks associated with this procedure include infection, damage to the vagus nerve or breathing problems.
These are a few of the many studies in progress by researchers in the search of effective treatment for people with different mental illnesses. However, some have argued that scientists should not label conditions that are unexplainable in medical terms lest they bring confusion not only in the categorization of the different mental illnesses but also in the treatment process.








Comments
Post a Comment